Batteries are used in a wide range of applications, from small toys to cars. We buy batteries depending on the device or application we are going to use them for. In this article you will learn about the most commonly used types of batteries in the world, their applications and how to care for them.
It is one of the most common types of primary cell. It draws its energy from a chemical reaction between zinc metal and manganese dioxide. Alkaline batteries have a higher energy density and a longer service life than other batteries, such as zinc-carbon batteries.
This type of battery is the most common type of battery used in cars and solar storage devices. This is because lead-acid batteries provide high current and are relatively inexpensive. However, it can only store about 25 watt hours per kilogram. Each cell in a lead-acid battery consists of an electrode immersed in a sulphuric acid solution. The lead electrodes are usually coated with lead oxide. When six of these cells are connected in series, a 12 V battery is provided. 3.
Lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used batteries today. They are used in a variety of computers, computing devices and thousands of consumer electronics such as smartphones, laptops etc. Research is underway to adapt this type of battery to other applications as they have a higher power density. The batteries maintain approximately 150 Watt hours/kg (150 Watt hours per kg).
The electrodes are mostly made of lithium and cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) with graphite and a solid lithium electrolyte.
The battery voltage is high, up to 4 V. This is mainly used to transport the partially reduced Li+;-partially reduced lithium cobalt oxide on graphite.
This type of battery can easily explode if exposed to high temperatures. There is currently research in this area as well. It is focused on revealing new and better electrode materials suitable for the electrolyte in order to improve the thermal stability of these batteries in larger applications.
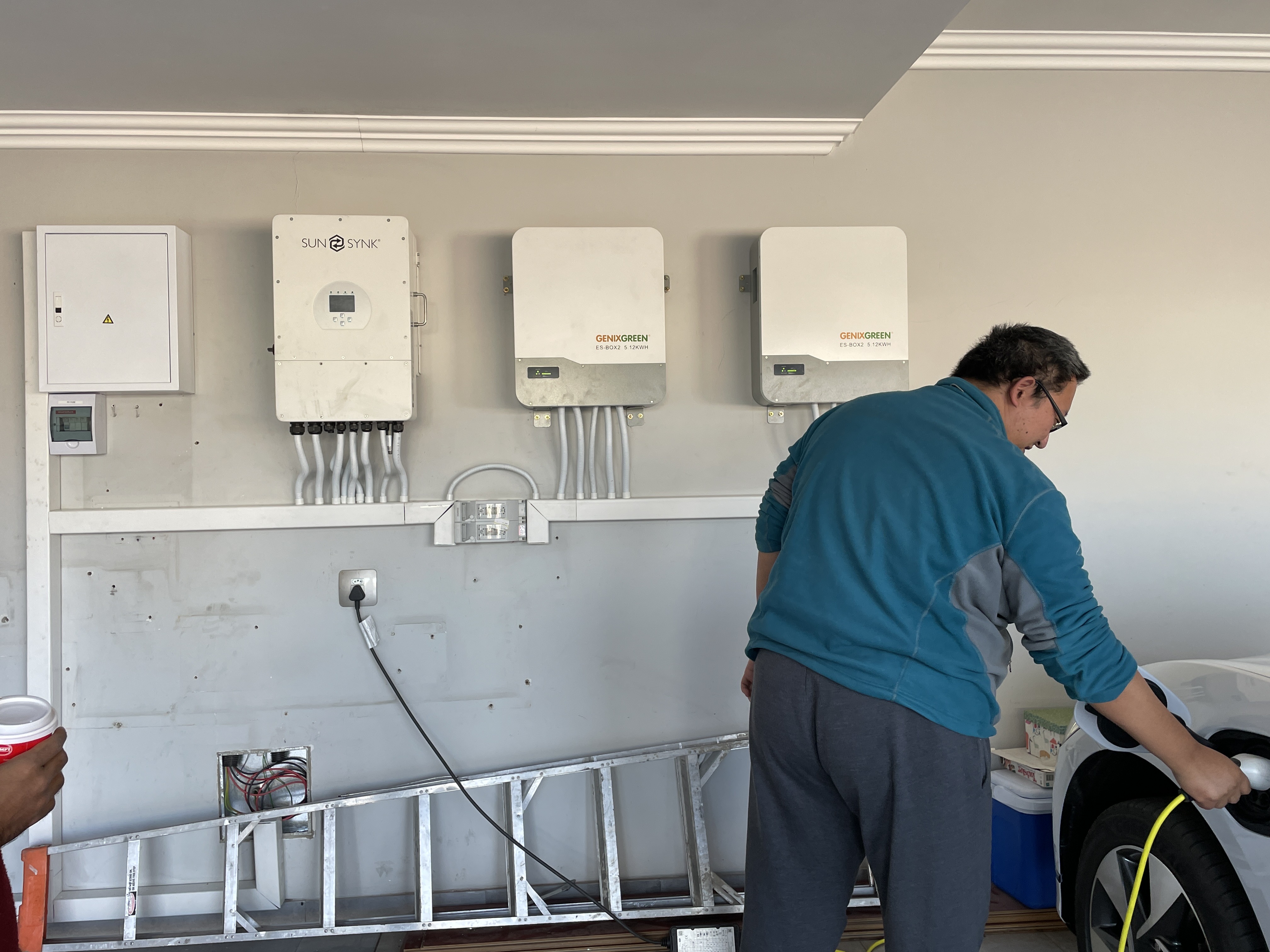

The metal for NiMH batteries is usually intermetallic AB5. "A" is a mixture of rare earths, including praseodymium, lanthanum, neodymium and cerium. "B" stands for manganese, nickel, cobalt and/or aluminium. These types of batteries have storage capacities of up to 100 watt-hours per kilogram and are even more thermally stable than lithium-ion batteries. Some of these types of batteries are designed for use in hybrid vehicles.
Alkaline batteries are easily the most widely used type of battery in the world, with significant consumption in the USA, the UK and even Switzerland. They are designed for long-lasting performance. These cells can be found in remote controls, radios and clocks. Due to their long running time, alkaline batteries are ideal for digital cameras, MP3 players, handheld games, etc.
The main applications for lead-acid batteries are usually in automotive starting, light weighting and ignition systems (also known as SLI). Another form of battery - the wet cell - is used as a back-up power source for high-end servers, PCs, telephone exchanges and off-grid homes using inverters. Lead-acid batteries are also used in portable emergency lights.
These are usually long-life batteries and they are used in portable consumer electronics such as calculators, digital diaries, watches, iPods, stopwatches, toys and even artificial pacemakers. Lithium batteries can also be used to replace alkaline batteries in a variety of applications such as clocks and cameras. Lithium batteries may be more expensive, but they have a much longer lifespan.
This type of battery is available in all standard sizes and has a high power density. They are easy to recharge and are a good alternative to alkaline batteries. They are used in applications very similar to alkaline batteries and are also rechargeable. They can also be used for all applications of NiCd batteries.
In the following paragraphs we will list how to care for the different battery types. Each battery type requires the same basic maintenance. Therefore, we will not list the basics, as it is expected that every battery user should know these. We will therefore list additional battery maintenance, please feel free to apply them to your batteries where applicable.
If you have a data logger, it can be programmed to measure, record and transmit the battery voltage at regular intervals. Recording the minimum daily battery voltage is a good way to check the condition of your battery. In fact, your data logger can be programmed to record the number of times the battery voltage drops below a specific value.
It is important to note that temperature and a number of other factors can affect your battery's performance. It is therefore important to monitor the battery voltage.
If properly connected to the device, the blocking diode in the system prevents the user supplied battery from charging the alkaline batteries. Therefore, alkaline batteries cannot be charged and the battery manufacturer does not recommend attempting to charge them. If a back-up power supply is required, use user-supplied sealed batteries.
You must ensure that your alkaline batteries do not leak. Please try the following tips to ensure this;
" Store alkaline batteries in a temperature range of -25°C to + 50°C.
" Do not mix used alkaline batteries with new alkaline batteries.
" If connected to a data logger, keep the alkaline batteries at a minimum voltage of 9.6 V.
If two batteries are to be connected in parallel, ensure that two different batteries with multiple ampere-hour ratings are not connected in parallel.
If lead-acid batteries are left discharged for long periods of time, large sulphate crystals may form, which can negatively affect the performance of the battery. To avoid this, recharge the stored batteries every few months. 6.
In snowy and cold climates, it is recommended that you store your batteries in an isolation box or battery compartment. This is to protect them from extreme temperatures.
You should also ensure that you install the solar panels in such a way that there is no room for snow, as this can block energy and cause some stress in the system.