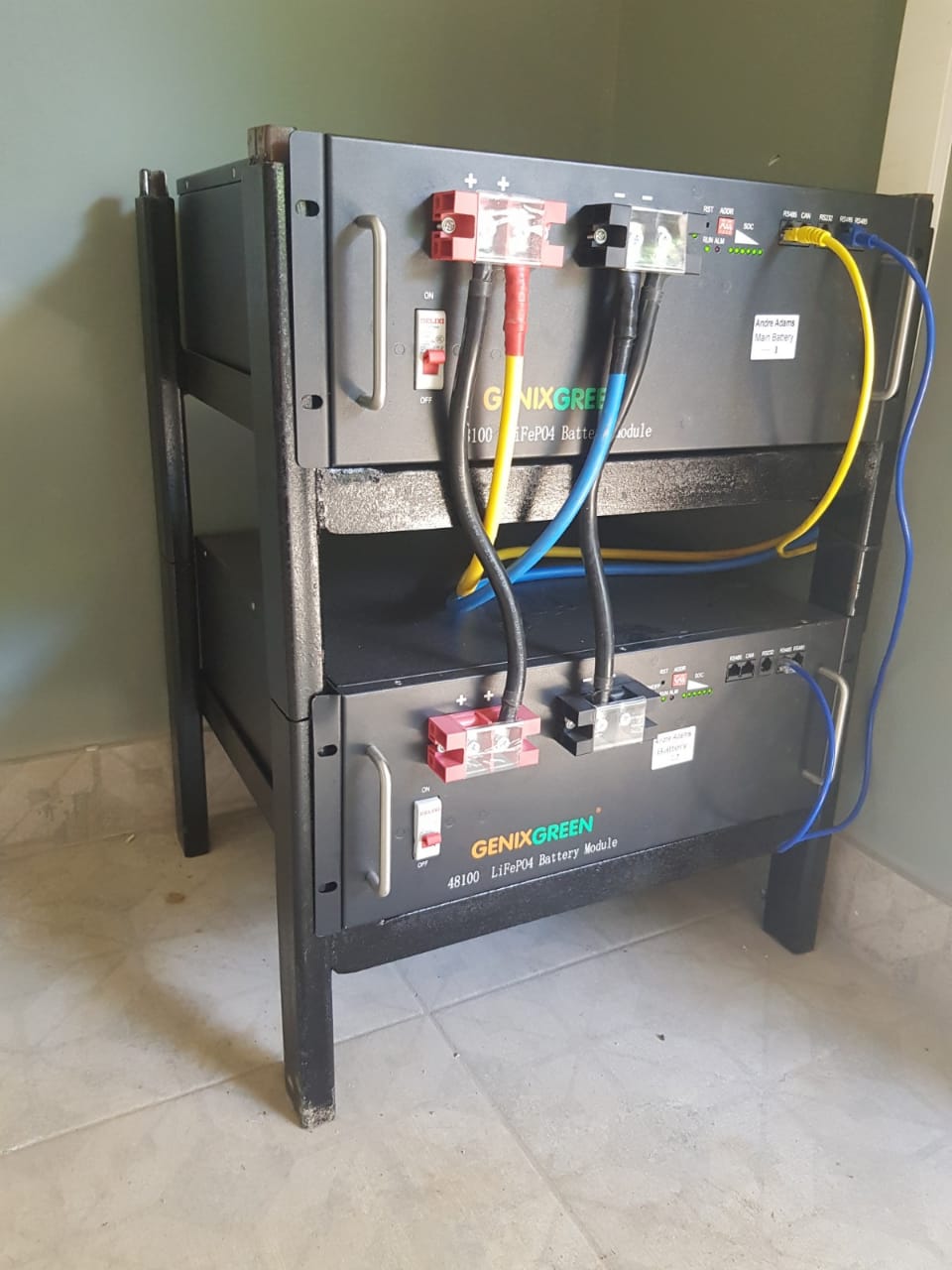
Lithium-ion batteries are mainly composed of positive electrode materials, negative electrode materials, electrolytes, separators, positive electrode current collectors, and negative electrode current collectors.
The negative electrode of lithium-ion batteries is generally made of graphite or other carbon materials.
The cathode is a transition metal oxide such as lithium cobalt oxide.
Both graphite and lithium cobalt oxide have a layered structure, and lithium ions can embed or detach from this layered structure at specific voltages without irreversible changes in the material structure.

The carbon structure of the negative electrode is mainly arranged in a graphite structure, and during charging, the lithium ions are embedded in the graphite structure, so for the burden electrode, an embedded reaction occurs.
At the time of charging input, the lithium atoms in the positive electrode ionize into lithium ions and electrons. Then
The lithium ions migrate from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the electrolyte under the action of the applied electric field for reaction and reduction to lithium atoms, which are subsequently inserted into the laminate structure of the negative graphite thereby forming a charge.
When the battery is discharged, the lithium ions in the carbon material forming the anode move through the diaphragm to the cathode material (lithium compound) and a discharge current is passed.
At the time of discharge output, the lithium atoms ionize ions and electrons on the surface of the negative electrode and flow to the positive electrode through the electrolyte and load respectively, and then recombine into lithium atoms at the positive electrode and insert into the layer structure of lithium cobalt oxide at the positive electrode to form a discharge.
Lithium ion batteries work by charging input, the lithium ions migrate from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the electrolyte under the action of electric field for reaction and then inserted into the negative graphite laminate structure to form a charge. At the discharge output, the lithium atoms are recombined into lithium atoms at the positive electrode and then inserted into the lithium cobalt oxide layer at the positive electrode to form a discharge.
Previous: what are lithium batteries found in?